Integrative Medicine Case Reports, Volume 1, Issue 1 (January), 2020
Integrated approach of yoga therapy towards morbid obesity: A case report
KEY WORDS |
ABSTRACT |
|
Obesity grade 3
|
The present case study is of evaluation of Grade 3 obesity who visited the Arogyadhama (SVYASAUniversity, Bangalore). Conversations with the patient uncovered that the patient was being treated for obesity and patient portrayed his capacity to deal with the mental pressure related with overweight. He credited it to the inspirational demeanor created by his Yoga practice for 48 days. The patient was additionally ready to decrease body weight. The present narrative is an endeavor to give IAYT Practices, detoxification through Naturopathy.
doi: 10.38205/imcr.010139 |
|
*Corresponding Author:
|
Introduction
Overweight and obesity are characterized as unreasonable fat accumulation that is hazardous to wellbeing. An unrefined proportion of obesity is the weight record of BMI, an individual’s weight (in kilograms) separated by the square of their stature (in meters). An individual with a BMI of at least 30 is commonly viewed as Obesity grade 3. An individual with a BMI equivalent to or more than 25 is regarded as overweight.
Overweight and obesity are significant risk factors for various disorders, including diabetes, cardiovascular ailments and malignant growth (1).
Yoga reasoning and practice was first codefied by Patanjali to the great content, Yoga Sutras are broadly recognized as the legitimate content on Yoga. Yoga is a type of mind-body wellness that includes a blend of strong action and a coordinated attention to oneself, the breath, and vitality. Yoga is perceived as a type of mind-body practice that coordinates a person’s physical, mental and profound segments to improve parts of wellbeing, especially stress related ailments (2).
In 2016, more than 1.9 billion grown-ups matured to 18 years while the more seasoned were found to overweight. Of these more than 650 million grown-ups were large. In 2016, 39% of grown-ups matured 18 years and over (39% of male and 40% of female) were overweight. Overall, about 13% of the world’s grown-up population (11% of male and 15% of female) were fat in 2016. The overall predominance of heftiness almost significantly increased somewhere in the range of 1975 and 2016.
In 2016, an expected 41 million kids younger than 5 years were overweight or fat. Overweight and heftiness are presently on the increase in low-and middle income nations, especially in urban settings. In Africa, the degree of overweight youth, under 5, has expanded by almost 50 percent since 2000. More than 340 million kids and young people matured to 5–19 were overweight or in 2016.
The predominance of overweight and weight among youngsters and teenagers matured in the age group of 5–19 has risen drastically from only 4% in 1975 to simply over 18% in 2016. The increase has happened comparably among the two young men and young ladies: in 2016, 18% of young ladies and 19% of young men were overweight. While under 1% of children and adolescents aged 5–19 were obese in 1975, more than 124 million children and adolescents (6% of girls and 8% of boys) were reported obese in 2016.
Overweight and obesity are known to be the primary contributing factors for deaths worldwide than underweight. Globally, there are more people who are obese than underweight – this occurs worldwide except parts of sub-Saharan Africa and Asia (3).
The etiology of obesity is unquestionably more unpredictable than just an uneveness between vitality admission and vitality yield. In spite of the fact that this view permits simple conceptualization of the different instruments engaged with the advancement of obesity, factor is undeniably more than just the consequence of eating excessively as well as practicing pretty much nothing (sedentary lifestyle). Potential factors in the advancement of obesity are the following:
• Metabolic factors
• Genetic factors
• Level of activity
• Endocrine factors
• Race, sex, and age factors
• Ethnic and cultural factors
• Socioeconomic status
• Dietary habits
• Smoking cessation
• Pregnancy and menopause
• Psychological factors
• History of gestational diabetes
• Lactation history in mothers
Developing information suggests that a striking incendiary, and potentially infective, etiology may exist for obesity. Fat tissue is known to be a vault of different cytokines, particularly interleukin 6 and tumor putrefaction factor alpha. One investigation indicated a relationship among obesity and a high-typical degree of plasma procalcitonin, a needy variable that mirrors a condition of pain or irritation. Data has demonstrated that adenovirus-36 is related with obesity in chickens and mice. In human examinations, the pervasiveness of adenovirus-36 disease is 20–30% in individuals who are obese, versus 5% in individuals who are not over weight (4).
Case presentation
Recruitment of patient

A 28 year old male participant from New Delhi, enrolled himself at Prashanthi Kutiram on the 15th of June 2018 and was put in section ‘H’, which deals with Obesity. He resided in campus from 15.06.2018 to 02.08.2018 (48 days). He underwent Yoga therapy with some detoxification treatments like sauna bath, steambath, hip bath and underwater massage as well as for more relaxation and aids more benefits Mud pack to abdomen and eyes for a week in between.
IAYT protocol: Treatment regimen
S. No. |
Loosening practice |
Duration of procedure |
Frequency |
Duration of intervention |
1 |
Butterfly |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
2 |
Loosening of Fingers & wrist |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
3 |
Padasancalana |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
4 |
Loosening of elbow |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
5 |
Side bending |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
6 |
Shoulder Rotation |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
7 |
Twisting |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
8 |
Spinal Twisting |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
9 |
Neck movement |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
10 |
Rotation |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
11 |
Ardhakati Chakrasana |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
12 |
Sideward bending |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
13 |
Spinal twist |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
14 |
Hip stretch |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
15 |
Back stretch with alternate leg |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
16 |
Full butterfly |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
17 |
Alternate & both leg raising |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
18 |
Side leg raising |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
19 |
Cycling |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
20 |
Pavanamuktasanakriya |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
21 |
Lumber stretch |
10 |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
Suryanamaskara (7)
S. No. |
Suryanamaskara |
Duration of procedure |
Frequency |
Duration of intervention |
1 |
Hastauttanasana Pádahastásana Aswasancalanasana Tulasana Sasankasana Sastanganamaskar Bhujangasana Parvatasana Sasankasana Aswasancalanasana Pádahastásana Hastauttanasana |
12 |
24 times a day |
8 weeks |
S. No. |
Pranayama |
Duration of procedure |
Frequency |
Duration of intervention |
1. |
Nadishuddhi Pranayama: Nādiśuddhi pranayama balances both the lobes equally which restores the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. |
9 Rounds for each nostril |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
2. |
Brahmari:Brahmari gives soothing effect to the entire brain. |
9 Rounds |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
3 |
Naadaanusandhna: Breathing exercises, sectional breathing strengthens and soothes the entire nervous system restoring balance to a depleted and imbalanced autonomic nervous system |
5 Rounds |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
Mind Sound Resonance Technique (MSRT) (10)
Advanced Yoga technique MSRT which is developed by SVYASA to specifically strengthen the immune defence, to develop will power and there by promote health and happiness was done once a day.
Deep Relaxation Technique (DRT) (11)
Each session of passive exercise, pranayama was completed with DRT.
DRT is a deeper and more intense form of relaxation. The entire body and the mind move together, connecting with each other while the breathing plays a crucial role to bring this connection. The main features of this form of relaxation technique are:
DRT is done in Savasana (Corpse Pose) and is best done at the end of the Yoga practice to release all the tensions while retaining the muscle strength. It is done longer and is generally for a minimum of 15 minutes. It is always done with the instructions given by a Yoga teacher. DRT can also be done anytime during the day provided the time gap between meals is minimum 2+hours. It can also be done by anyone even without the practice of Yoga poses.
DRT is considered a base pose as deep relaxation technique variations can be derived from this pose.
Breathing practices
S. No |
Breathing practices |
Duration of procedure |
Frequency |
Duration of intervention |
1 |
Hand Stretch Breathing |
2 minutes |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
2 |
Hands In and Out Breathing |
2 minutes |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
3 |
Ankle stretch Breathing |
2 minutes |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
4 |
Tiger Breathing |
2 minutes |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
Yogasana (12)
S. No. |
Yogasanas |
Duration of procedure |
Frequency |
Duration of intervention |
|
Standing position |
|
|
|
1. |
Ardhakati Chakraasana: Reduces fat in waist region, stimulates the sides of the body. Give lateral bending to the spine. |
2 minutes |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
2. |
Ardha Chakraasana:Makes the spine flexible, stimulates the spinal nerves, promotes circulation of blood into head. Strengthens the neck muscles. Expands chest and shoulders. Improves breathing. |
2 minutes |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
|
Sitting position |
|
|
|
3. |
Vakrasana: Lateral twist gives flexibility to the spine, tones up the spinal nerves. Helps to cure constipation. Improves lung capacity. |
2 minutes |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
|
Prone position |
|
|
|
4. |
Bhujangasana: Brings flexibility to the dorsal spine. Strengthens the spinal muscles. Reduces the abdominal fat. |
2 minutes |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
|
Shalabhasana: Helpful in managing sciatica and low back ache. Reduces fat on thighs and buttocks. |
2 minutes |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
|
Supine position |
|
|
|
|
Sethubandhasana: The extensor muscles of the back grow powerful and the hips are contracted and hardened. The asana strengthens the neck and tones the cervical, dorsal, lumbar and sacral regions of the spine. |
2 minutes |
2 times a day |
8 weeks |
Diet Protocol
Participant completely underwent a Naturopathic diet includes raw diet (fruits, Salad, Sprouts and buttermilk), Boiled diet (Boiled vegtables, Chapati, Rice, Dal and Butermilk) as well as planed frequent juice therapy and fruit diet and also underwent a Naturopathy treatment for detoxification for a week in starting (6 days).
Naturopathy diet:
|
8:00 am |
10:00 am |
12:00 pm |
2:00 pm |
5:00 pm |
7:30 pm |
8:30 pm |
1st day |
Juice |
Juice |
Boiled diet |
Juice |
Juice |
Boiled diet |
Kashayam |
2nd day |
juice |
juice |
Raw diet |
juice |
juice |
Raw diet |
Kashayam |
3rd day |
Juice |
Juice |
Juice |
Juice |
Juice |
Juice |
Juice |
4th-6th day |
Lemon honey juice fasting |
||||||
7th day |
juice |
juice |
Raw diet |
juice |
juice |
Raw diet |
Kashayam |
8th day |
juice |
juice |
Raw diet |
juice |
juice |
Raw diet |
Kashayam |
9th-13th day |
Lemon honey juice fasting |
||||||
14th day |
juice |
juice |
Raw diet |
juice |
juice |
Raw diet |
Kashayam |
15th day |
juice |
juice |
1 apple |
juice |
juice |
1 apple |
Kashayam |
16th -22nd day |
Lemon honey juice fasting |
||||||
23rd day |
juice |
juice |
1 apple |
juice |
juice |
1 apple |
Kashayam |
24th day |
juice |
juice |
Raw diet |
juice |
juice |
Raw diet |
Kashayam |
25th day |
juice |
juice |
1 apple |
juice |
juice |
1 apple |
Kashayam |
26th-30th day |
Lemon honey juice fasting |
||||||
31st-32nd day |
juice |
juice |
1 apple |
juice |
juice |
1 apple |
Kashayam |
33rd day |
juice |
juice |
Raw diet |
juice |
juice |
Raw diet |
Kashayam |
34th day |
juice |
juice |
Boiled diet |
juice |
juice |
Boiled diet |
Kashayam |
35th day |
juice |
juice |
Raw diet |
juice |
juice |
Raw diet |
Kashayam |
36th day |
juice |
juice |
1 apple |
juice |
juice |
1 apple |
Kashayam |
37th day -44th day |
Lemon honey juice fasting |
||||||
45th day |
juice |
juice |
1 apple |
juice |
juice |
1 apple |
Kashayam |
46th day |
juice |
juice |
Raw diet |
juice |
juice |
Raw diet |
Kashayam |
47th day |
juice |
juice |
Raw diet |
juice |
juice |
Raw diet |
Kashayam |
48th day |
juice |
juice |
Boiled diet |
juice |
juice |
Boiled diet |
Kashayam |
|
8:00 am |
10:00 am |
12:00 pm |
2:00 pm |
5:00 pm |
7:30 pm |
8:30 pm |
Saturday |
Ashguard juice |
Bitterguard juice |
Lunch |
Lemon honey juice |
Papaya juice |
Dinner |
Kashayam |
Sunday |
Carrot juice |
Watermelon |
Lunch |
Lemon honey |
Musk melon Juice |
Dinner |
Kashayam |
Monday |
Bottleguard juice |
Musk melon |
Lunch |
Buttermilk |
Papaya Juice |
Dinner |
Kashayam |
Tuesday |
Methi water |
Pinapple Juice |
Lunch |
Lemon honey |
Carrot juice |
Dinner |
Kashayam |
Wedensday |
Ash guard juice |
Carrot juice |
Lunch |
Lemon honey |
Papaya juice |
Dinner |
Kashayam |
Thursady |
Carrot juice |
Ash guard |
Lunch |
Buttermilk |
|
Dinner |
Kashayam |
Friday |
Breakfast |
– |
Pongal+buttermilk |
– |
– |
Dinner |
– |
Lunch (boiled diet) 1 chapati, 1 cup adl, 1 cup rice, buttermilk, 100gm boiled
vegtables (beans+pumkine+beatroot+methi+spinach+knolkhol)
Dinner: (raw diet) 2-3 slices fruits(papaya+watermelon+pomegranate/muskmelon), Vegetable salad (cucumber+pomegranate+beatroot+carrot), sprouts (Moong+groundnuts), Buttermilk
Naturoapthy Treatment chart (only for 1 week in a starting of protocol for detoxification)
|
8:00 am |
2:00 pm |
Saturday |
Mud pack to abdomen and eye |
Full mud bath |
Sunday |
– |
Cold under water massage |
Monday |
Mud pack to abdomen and eye |
Full body massage |
Tuesday |
– |
Vibromsg to abdomen and thigs+sauna bath |
Wednesday |
Mud pack to abdomen and eye |
Cold hip bath+GH Pack |
Thursday |
Mud pack to abdomen and eye |
Sauna bath+Vibromsg to abdomen |
Diagnosis
Progression of Obesity was detected by his Anthropometric
measurements, whose reports were provided by the patient.
Parameters |
DOA |
DOD |
Parameters |
DOA |
DOD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Pulse Beats/min |
86 bpm |
70 bpm |
Weight in kg |
142 kg |
121.6 kg |
BP in mmHg |
150/100 mm/Hg |
130/90 mm/Hg |
Height in mt |
172 cm |
*** |
Respiratory Cycles/min |
16 cpm |
16 cpm |
BMI [Kg/mt2] |
47.99 |
42.2 |
Bhramari Time (Sec) |
9 sec |
9 sec |
Mid arm circumference |
42 cm |
37 cm |
Symptoms score |
0 |
0 |
Waist circumference |
144 cm |
136 cm |
Medication score |
0 |
0 |
Hip circumference |
136 cm |
129 cm |
Vital data and Anthropometric measurements:
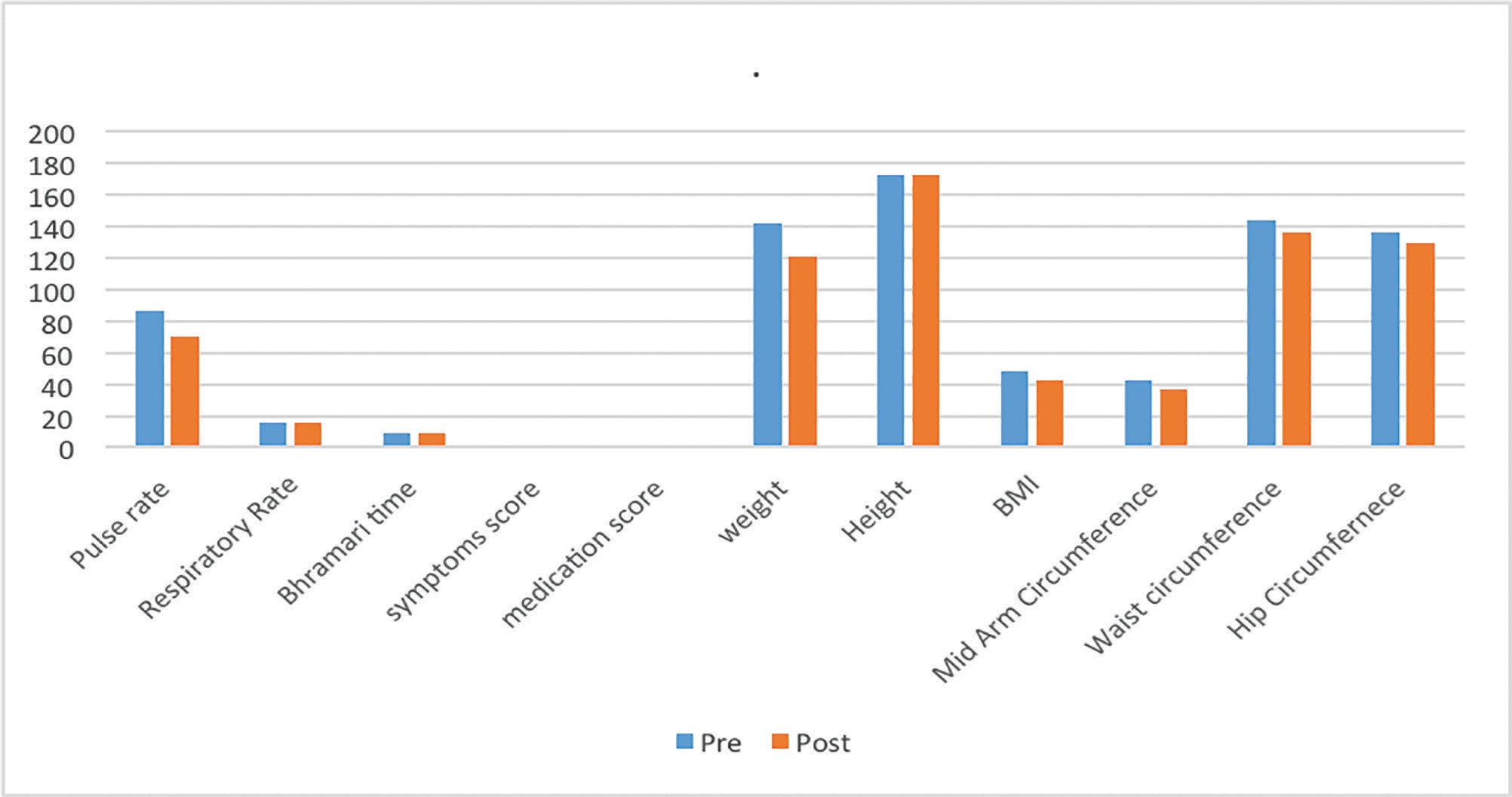
The patient was able to lose 20.4 Kgs of weight after following the above treatment regimen as well as regulation of Pulse rate and respiratory rate take place. Blood pressure got marked in range that is 130/90 mm/hg compare to before treatment. Respiratory rate remain regular and same after the treatment. There will be drastic reduction in weight and anthropometric measurements that includes mid arm circumference from 42 cm to 37 cm, Hip circumference 136 cm to 129 cm and Waist circumference from 144 cm to 136 cm as well as marked reduction in overall Body mass index from 47.99-42.2 Kg/(M)2.
Discussion
The weight of patients has been accounted to increase since a long time. Aggravating factor is the absence of physical movement and life style. Anthropometric parameters have indicated that a patient belongs to grade 3 obesity. It is anticipated that the patient had the option to keep up a consistent body weight by receiving IAYT (Integrated methodology of Yoga treatment) which may have forestalled weight gain. During his stay, he experienced Integrated approach of Yoga treatment just as Naturopathy for Detoxification and Diet treatment moreover. Naturopathy helps to keep up balance between medicines and diet. Naturopathy enables improvement in fat digestion just as perspiration by follow up on waste framework. Patient used to practice Pranamyama (daily once), Yoga special technique day by day two sessions, (Weight decrease) just as Kriya (weekly twice). Overall, Yoga helped him to keep up physical wellbeing just as emotional well-being.
Conclusion
A case of a 28 year old male of Grade 3 Obesity was conservatively managed using principles of Yoga therapy with Naturopathy as proposed by the SVYASA. By following the Obesity based protocol, the patient was successful to lose 20.4 Kgs and attain the desirable target set at the beginning of the month. It is, therefore, proposed that further prospective studies be carried out using Yoga therapy so that an evidence-based model of obesity protocol can be formulated for all patients in this age group.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the following people who played an instrumental role in the completion of this project. We grateful to Dr. Nagarathna and Dr. Amit Singh of research for sharing their thoughts with other people. We Would also like to thank Mr. Sumit Aundhekar for extending his support throughout our work.
Authorship contribution
RPJ: has written article.
RN: guided to write article
AS: has contributed in a treatment planning.
Informed consent form
Yes
Source of funding
Nil
Conflict of interest
Nil
Received Date: 01-11-19; Revised Date: 11-02-20;
Accepted Date: 13-02-20
References
1. Telles S, Sharma SK, Singh A, Kala N, Upadhyay V, Arya J, Balkrishna A. Quality of Life in Yoga Experienced and Yoga Naïve Asian Indian Adults with Obesity. Journal of obesity. 2019;2019.
2. Verma A, Shete SU, Doddoli G. An integrated therapy approach for the management of obesity-associated disorders: A case report. Journal of family medicine and primary care. 2019 Apr;8(4):1491.
3. Mohamad WB, Mokhtar N, Mafauzy M, Mustaffa BE, Musalmah M. Prevalance of obesity and overweight in northeastern peninsular Malaysia and their relationship with cardiovascular risk factors. The Southeast Asian journal of tropical medicine and public health. 1996 Jun;27(2):339–42.
4. Atkinson RL. Viruses as an etiology of obesity. InMayo Clinic Proceedings 2007 Oct 1 (Vol. 82, No. 10, pp. 1192–1198). Elsevier.
5. Mazur A, Matusik P, Revert K, Nyankovskyy S, Socha P, Binkowska-Bury M, Grzegorczyk J, Caroli M, Hassink S, Telega G, Malecka-Tendera E. Childhood obesity: knowledge, attitudes, and practices of European pediatric care providers. Pediatrics. 2013 Jul 1;132(1):e100-8.
6. Dushyant S, Padmini T, Ganpat TS, Ramarao NH. An innovative approach in health sciences: Yoga for obesity. Archives of Medicine and Health Sciences. 2015 Jan 1;3(1):162.
7. Nautiyal R. Effect of Surya Namaskar on weight loss in obese persons. Int. J. sci. and consciousness. 2016;2(1):1–5.
8. PA B. Effects of yoga-pranayama practices on metabolic parameters and anthropometry in type 2 diabetes. International Multidisciplinary Research Journal. 2011 Oct 10.
9. Gokal R, Shillito L, Maharaj SR. Positive impact of yoga and pranayam on obesity, hypertension, blood sugar, and cholesterol: a pilot assessment. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. 2007 Dec 1;13(10):1056–8.
10. Dhananjai S, Sadashiv ST, Dutt K, Kumar R. Reducing psychological distress and obesity through Yoga practice. International journal of yoga. 2013 Jan;6(1):66. S, Dutt K, Kumar R, Dhananjai S, Sadashiv. Reducing psychological distress and obesity through Yoga practice. Int J Yoga. 2013;
11. Bernstein AM, Bar J, Ehrman JP, Golubic M, Roizen MF. Yoga in the management of overweight and obesity. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine. 2014 Jan;8(1):33–41.
12. Seo DY, Lee S, Figueroa A, Kim HK, Baek YH, Kwak YS, Kim N, Choi TH, Rhee BD, Ko KS, Park BJ. Yoga training improves metabolic parameters in obese boys. The Korean Journal of Physiology & Pharmacology. 2012 Jun 1;16(3):175–80.