Case Report
Integrative Medicine Case Reports, Volume 3, Issue 1 (January), 2022
Integrative treatment on Crohn’s disease: A case report
K. S. Nibedita1, Reshma P. Jogdand2, Bhavit Bansal3, Amit Singh4 and R. Nagarathna5
1Arogyadhama VYASA Bangalore, India
2,4,5Department of Life sciences, SVYASA University, Bangalore, India
3The School of Yoga and Naturopathic Medicine, SVYASA University, Bangalore, India
| |
|
|
KEY WORDS |
|
ABSTRACT |
Crohn’s disease
Yoga therapy
Ayurveda
Naturopathy
Diet therapy
Quality of life |
|
A 27 year old female patient with multiple symptoms like pain in the abdomen, loose motions vomiting, headache, fatigue presented at a residential integrative medicine facility at Bangalore, India. The patient was a known case of Crohn’s disease since 3 years. The patient was administered with an individualized tailored Integrative medicine protocol for duration of 8 weeks. The protocol included yoga sessions, Diet therapy and individualized Ayurveda and Naturopathy therapies as prescribed by the treating physician with an objective of a holistic approach. The results showed significant reduction in her symptoms and medication scores followingthe individualized protocol. Moreover, the patient reported satisfaction to therapy and improved overall quality of life at the semi-structured interview. The present case study underscores the effect of integrative medicine practices and advocates its effect as a standalone therapy for Cronh’s disease.
doi: 10.38205/imcr.030116 |
*Corresponding Author:
Reshma P. Jogdand
Department of Life sciences
SVYASA University, Bangalore, India
Contact no: +91-9449164937
E-mail: reshma@svyasa.edu.in |
Introduction
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease characterized by transmural inflammation that can affect the entire gastrointestinal tract from the mouth to the anus (1). Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract with variety of symptoms including diarrhea, constipation, bloating, pain abdomen and malena (2). The prevalence of Crohn’s disease is annually ranging from 3 to 20 cases per 100,000 (3). Crohn’s disease is more common in industrialized areas (4). Introducing side effects are variant from person to person, which includes loose motion, stomach pain, reduction in weight, fatigue, Fever, and cold (5). On average of 1.17 million grown-ups inside the US had Irritable Bowel Disorder. As per a study from 2013 in the local area, 565,000 were tortured by Crohn’s, and 593,000 were going through internal gastrointestinal disorders, such as IBD. As per the NIDD (National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases), regional enteritis appears to be more predominant. Specialists say that 3.1–14.6 of Crohn’s new cases are analyzed by doctors per 100,000 men a very long time in Disease Control and Prevention Centers. They additionally notice that in agricultural nations, IBD is more predominant. Anyone can get affected by Crohn, yet in youthful people, especially somewhere in the range of 20 and 29 years of age, it’s more normal. Smoking may increase twofold the probability of building up Crohn’s (6) indeed, even in individuals with a top to bottom relative with IBD.
Sage Patanjali first portrays yoga practices thorough Yoga sutras. He explained that Yoga is a mind-body medicine, which includes physical activity as Asana, Loosening Practice, Kriya and Mental awareness through Meditation, Pranayama, Breathing practices as well as Dharana and Dhanya. Yoga is perceived as a type of medicine that links Physical, Mental, Social wellbeing and has a significant impact on stress-induced ailments (7). As per Yogavasistha, diseases are of two types, Adhija vyadhi or Anadhija vyadhi. Adhija Vyadhi is explained as the diseases caused by stress. Psychological stress plays a pivotal role in the development of IBS. Therefore here, IBS can be considered as adhija Vyadhi and yoga therapy can play an important role in IBS. Previous literature have also highlighted the effect of Yoga on IBS symptom reduction. However, no study yet has reported the effect of an integrative medicine protocol among crohn’s disease patient. The current case study is an attempt to highlight the efficacy of the same in the desired population.
Case presentation
A 28-year-old female participant, Miss. XXX, approached a residential integrative medicine facility at Bangalore with the presenting complaints of weakness and sudden drop in weight since two months and loose motion with abdominal pain since 15 days. She also presented with headache with vomiting. She was finding it difficult to perform day today activities as well as low confidence in work. As per her the quality of life was really low and she had low self-esteem. She was admitted in the holistic healthcare center and was posted in the gastroenterology section. Initially a personalized 3 week integrative medicine based protocol was tailored for her. The intervention was planned after a discussion on her health status among a panel of doctors from various streams i.e. Yoga, Ayurveda, physiotherapy and naturopathy. A integrative protocol including yoga session, diet counselling, yoga and Ayurveda was planned for 3 weeks. After the end of first 3 weeks the patient extended her stay looking at the improvement of the health status for 4 more weeks. She became regular for therapy and her symptoms were gradually reduced. Table 1–4 depicts the detailed intervention with the duration. Following a detailed case history, initial counseling and obtaining signed informed consent, the intervention was planned by a team of consultants that included a physician, a naturopathy and yoga expert. Keeping a daily watch on the vital and blood parameters, the medications were tapered by the physician. We also conducted a semi structured interview to evaluate the satisfaction to therapy and quality of life.
Intervention
After a thorough evaluation, the integrative medicine protocol was planned. The Ayurveda and naturopathic therapies included a combination of matra vasti with external medication and oil application, therapeuticfasting and calorie restricted diet, hydrotherapy, mud therapy and manipulative therapies, with a focus on the detoxification. The therapies administered were modified based on the patient’s response assessed in the daily visit of the physician. Consideringthe involvement of the mind-body complex in the pathogenesis ofthe disease, an integrated yoga program was designed including asanas, pranayama, meditation, relaxation techniques, kriyas, educative lectures and yoga based counseling sessions (Table 1). Table 2 & 3 depicts the dietary modification and table 4 depicts the integrative medicine protocol and daily routine.
IAYT protocol
Treatment regimen
Table 1: Yoga therapy protocol
| Practices |
Duration of Practice |
Frequency |
Duration of Intervention |
Loosening Practice (8)
• Suryanamaskara
• Butterfly
• Loosening of Fingers & wrist
• Loosening of elbow
• Loosening of shoulder joint
• Loosening of toe and Ankle
• Ankle movement
• Hip rotation
• Waist rotation
• Neck movement
(sidewise, Forward, Backward, Rotation) |
15 min
5 min
4 rounds with breathing
4 rounds with chantting
4 rounds with hold
1 min
1 min
1 min
1 min
1 min
1 min
1 min
1 min
2 min |
Twice in a day |
8 weeks |
Breathing Practices (9)
Standing:
• Ankal stretch breathing
• Hands in and out breathing
Sitting:
• Shashankasana breathing
• Tiger breathing
Supine:
• straight leg raising breathing
• Lumbar stretch
Prone:
• Bhujangasana Breathing |
10 Min
1 min
1 min
1 min
1 min
1 min
1 min
1 min |
|
8 weeks |
Yogasana (10)
Standing:
• Tadasana
• Trikonasana
Sitting:
• Ardha matsyendrasana Gomukhasana
Prone:
• Triayakabhujangasan (Improves inner awareness and improves massaging effect to internal organs.)
• Shalabhasana
Supine:
• Ardha matsyasana
• Trikonasana |
15 min
All the asana prcedure with breathing awerness, Holding with chantting and maintain final position with normal breathing pattern |
|
8 weeks |
Pranayama (10)
• Nadishuddhi pranayama
• Bhramari Pranayama
• Nadanusandhana |
20 Min
10 min
4 min
6 min |
2 times in a day |
8 weeks |
Meditation
• Mind Sound Resonance Technique (11) |
30 min |
2 times in day
• Morning
• Before Bed |
8 weeks |
Relaxation Technique
• Deep Relaxation Technique (12) |
15 min |
After every session of Practice |
8 weeks |
Diet protocol
The participant was encouraged to take a naturopathic diet for the sequentially for 48 days of her visit in Prashanti kutiram. The schedule was as per the following.
Table 2: Diet plan
| 8:00 am |
10:00 am |
12:00 pm |
5:00 pm |
7:30 pm |
| Sprouts salad = Boiled green gram + Groundnuts + Horse gram/Fruits (watermelon + papaya + Apple + Pomogranate)/Vegetable juice |
Carrot juice/Cucumber juice |
2 Chapati + 1 cup brown rice + 1 cup day + 1 cup boiled mixed vegetables+Buttermilk/Curd |
Cooked carrot salad/carrot + beatroot soup without spices |
Vegetable khichadi (10./’ rice+20./’ rice+70 ./’ vegetables)/Vegeatble Daliya/Vegetable Oates |
Table 3: Diet guidelines
| Diet Guidelines |
| Low fibre food |
Boiled food, Boiled sprouts |
| More probiotic |
Curd, buttermilk |
Table 4: Treatment protocol
| Ayurveda and Naturopathy Treatment protocol for 20 days |
| 1st–10 days |
Mode |
Therapy |
Duration/Dose |
| Ayurveda Protocol |
External application |
Nabhimandal Basti with sahacharadi tailam followed by Murdu Abhayangam and Patra panda swedana these procedure reduces pain, increases the strength of muscle and improves generalised weakness |
|
| |
Internal usage |
Hinguashtak choorna
(it improves appetite and reduces the blotting)
Kamadughha Ras
Swarna Sootahesekhar Rasa |
½ tsp thrice/day with 1 tsp ghee
Before Breakfast
1–1 After food |
| Naturopathy |
External application |
7:00 am |
2:00–3:00 pm |
| |
|
Mud pack to eye and Abdomen
Mud pack to eye and Abdomen
Mud pack to eye and Abdomen
Mud pack to eye and Abdomen
Mud pack to eye and Abdomen
Mud pack to eye and Abdomen
Mud pack to eye and Abdomen with |
Gastro hepatic pack + partial msg to foot
Kidney pack + partial msg to neck and head
Cold abdomen pack + full body msg
Full body msg
Gastro hepatic pack + Foot msg
Kidney pack + partial msg to head and neck
Neutral Under water msg |
| 2nd–10 days |
Internal Treatment |
Neutral Enema
Juice Therapy |
alternative days |
| Ayurveda |
Internal |
Matra basti with yastimadhu tailam
Nalaparmadi tailam |
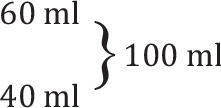
For 10 days |
| |
Internal |
Drashadi kashayam 10 ml + guduchyadi kashayam 10 ml + 20 ml water.
Ashwagandharistham 10 ml + Balaristham 10 ml + 20 ml water |
80 ml twice a day
Before Food
40 ml twice a day
After food |
| Naturopathy |
External application |
7:00 am |
2:00–3:00 pm |
| |
|
Mud pack to eye and Abdomen
Mud pack to eye and Abdomen
Mud pack to eye and Abdomen
Mud pack to eye and Abdomen
Mud pack to eye and Abdomen
Mud pack to eye and Abdomen
Mud pack to eye and Abdomen with |
Gastro hepatic pack + partial msg to foot
Kidney pack + partial msg to neck and head
Cold abdomen pack + full body msg
Full body msg
Gastro hepatic pack + Foot msg
Kidney pack + partial msg to head and neck
Neutral Under water msg |
| |
Internal Treatment |
Neutral Enema
Juice Therapy |
alternative days |
Diagnosis
Table 5: Vital parameters
| Parameters |
DOA |
DOD |
| Pulse Beats/min |
86 bpm |
70 bpm |
| BP in mmHg |
110/70 mm/Hg |
120/76 mm/Hg |
| Respiratory Cycles/min |
16 cpm |
16 cpm |
| Bhramari Time (Sec) |
9 sec |
12 sec |
| Symptoms score |
5 |
2 |
| Medication score |
5 |
0 |
At the end of 8 weeks, the post symptom checklist was filled. The comparison between pre and post data revealed a reduction in the symptoms and medicine scores. Table 5 and Figure 1 highlights the changes between pre and post data set. At the end of 8 weeks a semi structured interview was also conducted which revealed that the patient was highly satisfied by the therapy as there was a reductions in the symptoms. She also reported improved quality of life as well as faster return to day to day work schedule.
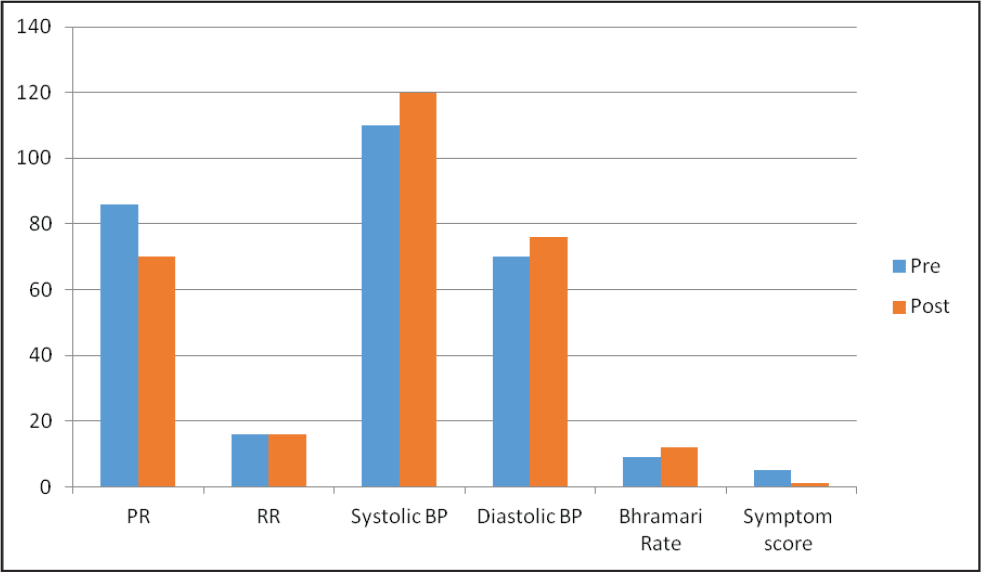
Figure 1: Pre post changes of vital parameters in graphic presentation
Discussion
Over one and half month of IAYT (integrated approach of yoga therapy) Naturopathy and Ayurveda treatment, the female participant was able to maintain a healthy living and shown improvement in the medication score. During her stay in prashanti kuteram she had undergone yoga technique practices, pranayama, cleansing practices, meditation, relaxation techniques and she followed the naturopathic diet which has effective in reducing symptoms related to gastro intestinal system by promoting alkalinity in blood and reducing acidic levels in blood. Ayurveda treatment is beneficial to reduces pain, increases the strength of muscle and improved generalized weakness. Overall treatment and Mind-body approach through yogic practices may have regulated the brain-gut axis and may have helped the participant for improving the digestive system, reduces stress level and to maintain a better quality of life.
Conclusion
Our findings show the importance of a simplified yoga intervention, Naturopathy treatment and Ayurveda treatment is a safe and effective complementary treatment in individuals with Chron’s disease.
Acknowledgment
First of all, I bestow in front of Lord Dhanavantari and express the deepest gratitude to the almighty. Also, I would like to acknowledge the following people who played an instrumental role in the completion of this project. I express my appreciation of the blessings of my gurus and salutations to my parents and all my teachers. I am grateful to Dr. Nagarathna and Dr. Amit Singh of research for sharing their thoughts with us.
Special thanks to a person who motivated me for this work, Dr. Amit Singh, his guidance and support makes me more strong and confident to study in this area. I am appreciative to section therapists for their guidance and allowing me to provide Yoga therapy to their patients and their immense support in my presented work. My love and regards go to my loving parents for their endless support and encouragement Finally, I express my gratitude to all the participants, as they were the true inspiration. Never the less the constant encouragement of Dr. Reshma J.
Authorship contribution
Dr. K. S. Nibedita, Dr. Reshma P. Jogdand, and Bhavit Bansal have written this article.
Dr. R. Nagrathna guided to write the article.
Dr. Amit Singh has contributed to treatment planning.
Informed consent
Yes.
Source of funding
Nil.
Conflict of interest
Nil.
Received Date: 11-06-21; Revised Date: 16-12-21
Accepted Date: 28-12-21
References
1. Feuerstein JD, Cheifetz AS. Crohn disease: epidemiology, diagnosis, and management. In Mayo Clinic Proceedings 2017 Jul 1 (Vol. 92, No. 7, pp. 1088–1103). Elsevier.
2. Cheifetz AS. Management of active Crohn disease. Jama. 2013 May 22;309(20):2150–8.
3. Molodecky NA, Soon S, Rabi DM, Ghali WA, Ferris M, Chernoff G, Benchimol EI, Panaccione R, Ghosh S, Barkema HW, Kaplan GG. Increasing incidence and prevalence of the inflammatory bowel diseases with time, based on systematic review. Gastroenterology. 2012 Jan 1;142(1):46–54.
4. Loftus Jr EV. Clinical epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: incidence, prevalence, and environmental influences. Gastroenterology. 2004 May 1;126(6):1504–17.
5. Feagan BG, Rutgeerts P, Sands BE, Hanauer S, Colombel JF, Sandborn WJ, Van Assche G, Axler J, Kim HJ, Danese S, Fox I. Vedolizumab as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. New England Journal of Medicine. 2013 Aug 22;369(8):699–710.
6. Hollander D, Vadheim CM, Brettholz E, Petersen GM, Delahunty T, Rotter JI. Increased intestinal permeability in patients with Crohn’s disease and their relatives: a possible etiologic factor. Annals of internal medicine. 1986 Dec 1;105(6):883–5.
7. Furukawa A, Saotome T, Yamasaki M, Maeda K, Nitta N, Takahashi M, Tsujikawa T, Fujiyama Y, Murata K, Sakamoto T. Cross-sectional imaging in Crohn disease. Radiographics. 2004 May;24(3):689–702.
8. Gupta N, Khera S, Vempati RP, Sharma R, Bijlani RL. Effect of yoga based lifestyle intervention on state and trait anxiety. Indian journal of physiology and pharmacology. 2006 Jan 21;50(1):41.
9. Sharma P, Poojary G, Dwivedi SN, Deepak KK. Effect of yoga-based intervention in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. International journal of yoga therapy. 2015;25(1):101–12.
10. Brown RP, Gerbarg PL. Sudarshan Kriya yogic breathing in the treatment of stress, anxiety, and depression: part I—neurophysiologic model. Journal of Alternative & Complementary Medicine. 2005 Feb 1;11(1):189–201.
11. Barrows KA, Jacobs BP. Mind-body medicine: an introduction and review of the literature. Medical Clinics. 2002 Jan 1;86(1):11-31.
12. Vempati RP, Telles S. Yoga-based guided relaxation reduces sympathetic activity judged from baseline levels. Psychological reports. 2002 Apr;90(2):487–94.